ISO 27001
Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection — Information security management systems — Requirements (Edition 3 – 2022)
Table of Contents
Abstract
ISO/IEC 27001 "specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining and continually improving an information security management system within the context of the organization. [ISO/IEC 27001] also includes requirements for the assessment and treatment of information security risks tailored to the needs of the organization ...”
[Source: ISO/IEC 27001:2022]
Introduction
The most recent version of the international standard for managing information security is ISO 27001:2022. In today’s digital landscape, where data breaches and cyber threats are increasingly common, organizations require a structured approach to protect sensitive information. ISO 27001:2022 gives a complete set of rules for setting up, running, keeping up with, and constantly improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
There are a few main reasons why organizations use ISO 27001:2022. First, it builds trust in the business by showing clients, partners, and stakeholders that keeping information safe is a top priority. Second, it helps businesses follow the law, rules, and contracts, which lowers the chance of getting in trouble or hurting their reputation. Third, it encourages a systematic way of managing risk, which lets businesses find, evaluate, and reduce security threats before they happen.
ISO 27001:2022 is one of the ISO 27000 standards. These standards give advice, terms, and best practices for protecting information. ISO 27001 sets the standards for an effective ISMS, but other standards in the family, like ISO 27002, give more specific instructions on how to set up security controls. The ISO 27000 series helps organizations build a strong, risk-based information security framework that follows the best practices used around the world.
Scope of ISO 27001:2022
The scope of ISO 27001:2022 sets the limits and uses for an organization’s Information Security Management System (ISMS). It says which parts of the organization, information assets, processes, and places are included in the standard. Clearly defining the scope is important for making sure that the ISMS deals with all relevant risks while still being practical and easy to use.
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 applies to all kinds of organizations, big and small, such as private companies, government agencies, healthcare providers, banks, and non-profits. Any business that deals with private data, like customer information, intellectual property, or operational records, can benefit from following the standard.
When determining the scope, organizations should consider factors such as business objectives, regulatory requirements, contractual obligations, and the needs of interested parties. The scope should also identify what is outside the ISMS, to ensure clarity and avoid misunderstandings during audits or certification assessments.
Organizations can effectively focus their resources, prioritize their risk management efforts, and show that they are following ISO/IEC 27001:2022 to both internal and external stakeholders by setting a clear scope. It sets up a clear structure for all the ISMS processes that come after it, like risk assessment, putting controls in place, and keeping an eye on things.
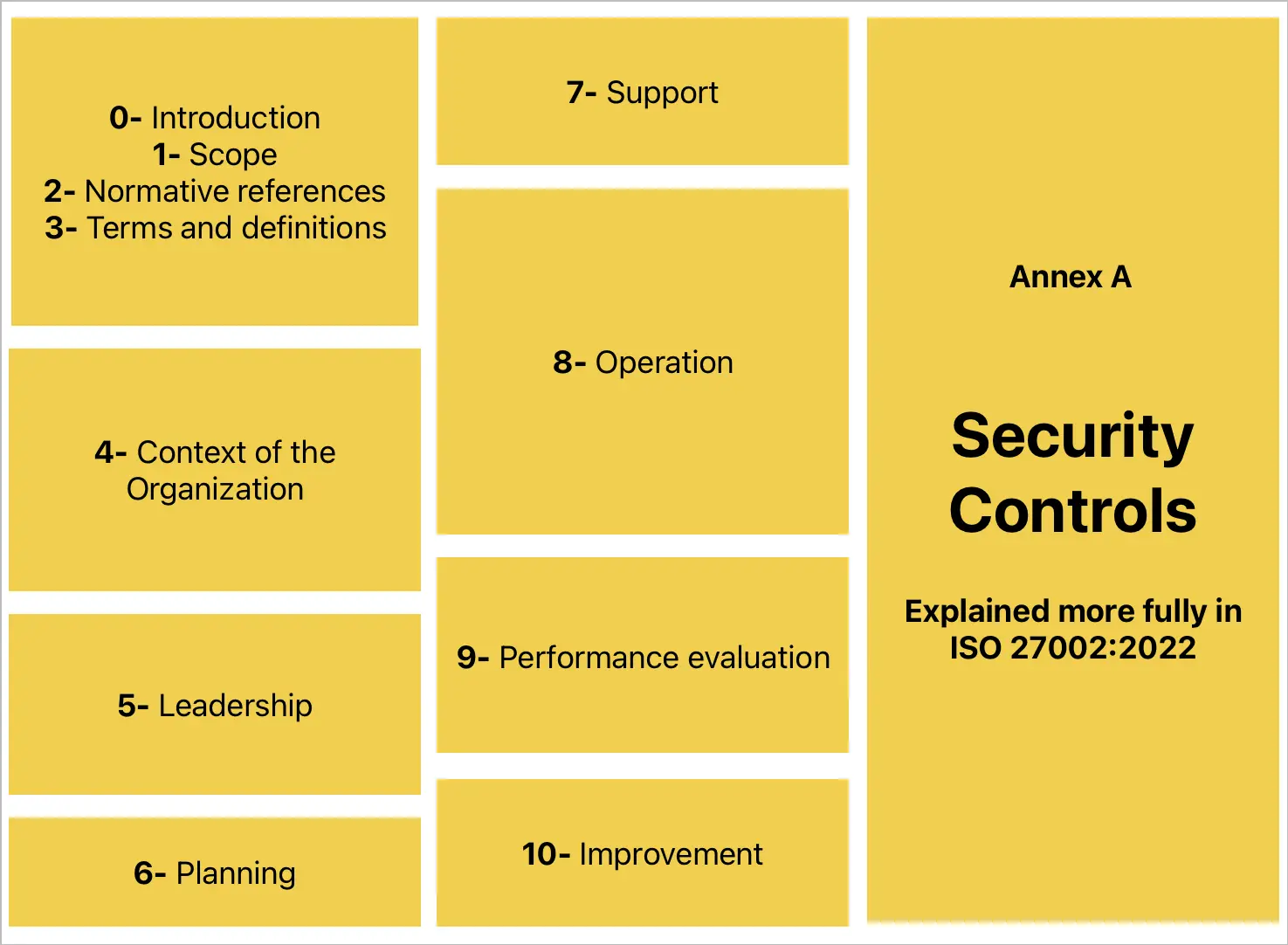
Structure of the Standard
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 has a clear and organized structure that fits with the Annex SL framework. This is a common high-level structure used in modern ISO management system standards. This alignment makes it easier for organizations to combine ISO/IEC 27001 with other ISO standards, like ISO 9001 (quality management) or ISO 22301 (business continuity).
The standard is divided into clauses 4 to 10, each addressing a different aspect of an Information Security Management System (ISMS):
- Clause 4 – Context of the Organization: Defines the internal and external factors that affect information security and identifies interested parties.
- Clause 5 – Leadership: Emphasizes top management’s commitment to information security, policy establishment, and role assignment.
- Clause 6 – Planning: Covers risk assessment, risk treatment planning, and setting information security objectives.
- Clause 7 – Support: Focuses on resources, competence, awareness, communication, and documented information.
- Clause 8 – Operation: Details the implementation of security controls and processes to mitigate risks.
- Clause 9 – Performance Evaluation: Addresses monitoring, measurement, internal audits, and management reviews.
- Clause 10 – Improvement: Guides continual improvement and corrective actions for maintaining an effective ISMS.
Additionally, Annex A provides a comprehensive list of 93 security controls, grouped into categories such as organizational, people, physical, and technological controls. While ISO/IEC 27001:2022 sets the requirements for an ISMS, Annex A serves as a practical reference for selecting and implementing appropriate controls based on risk assessment.
Understanding the structure of ISO/IEC 27001:2022 is essential for organizations to implement an effective ISMS and to prepare for certification audits. It ensures that all aspects of information security—from leadership commitment to continual improvement—are systematically addressed.
Key Updates in the 2022 Edition
ISO 27001:2022 has a number of important changes from the 2013 version. These changes are based on the changing world of information security and the needs of modern businesses. These changes make sure that businesses can still effectively manage risks and keep sensitive information safe.
1. Updated Annex A Controls:
The 2022 version puts the security controls into four groups: organizational, people, physical, and technological controls. This makes them easier to understand and use. New controls have been put in place to deal with modern threats. These include cloud security, threat intelligence, data masking, and information security for people who work from home.
2. Alignment with ISO 27002:2022:
ISO 27001:2022 is more in line with ISO 27002:2022, which gives detailed instructions on how to put in place information security controls. This alignment makes it easier to choose controls and makes sure that requirements and best practices are the same.
3. Structural and Terminology Changes:
The new standard uses more up-to-date language and gives clearer instructions on how to define the scope of an ISMS, assess risks, and set leadership responsibilities. It also gives businesses more freedom to use a risk-based approach that fits their needs.
4. Enhanced Focus on Risk and Opportunities:
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 stresses the importance of thinking about both risks and opportunities when managing information security. It encourages making improvements before problems happen instead of after they happen.
The 2022 version makes the standard more useful, flexible, and relevant for businesses that focus on digital and cyber issues. Companies that switch to ISO/IEC 27001:2022 will get clearer instructions, newer controls, and a stronger framework for dealing with information security risks.
Current Status and Transition Timeline
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 was officially published to replace the 2013 edition, providing updated guidance and controls to address evolving information security challenges. Organizations currently certified under ISO/IEC 27001:2013 need to be aware of the transition requirements and timeline to maintain compliance.
Publication and Adoption:
The 2022 edition is now the recognized standard for information security management systems (ISMS) worldwide. Certification bodies recommend organizations review and update their ISMS to align with the new requirements as part of regular audits or scheduled updates.
Transition Period:
A typical transition period allows organizations up to three years from the publication date of the 2022 edition to migrate from ISO/IEC 27001:2013. During this time, companies can continue to operate under the 2013 version while planning for the necessary updates in policies, controls, and documentation.
Guidance from Certification Bodies:
Certification bodies help with gap assessments, internal audits, and putting new or updated Annex A controls into place. Companies should start the transition early to avoid having to rush to meet compliance deadlines and to make sure the certification process goes smoothly.
Organizations need to know what the current status is and when the transition will happen in order to stay compliant, manage risks well, and make the most of the improvements that ISO/IEC 27001:2022 offers.